Experiment on changing my MTB handle bar with BMX! Its improve the comfort!
Recent newsUnbelievable! Its comfort actually!
read more(Comments)

I wish I knew earlier about this Google update! is something many site owners or marketers say on a daily basis. Moreover, it would be heaven on earth if we also knew how all those Google algorithm changes, be they official or unnamed updates, should be dealt with.
Most times, we get to see how rankings fluctuate, traffic drops, and still, we don’t know what to do. What’s more, we always think it’s us who made a mistake and, therefore, got downgraded. This blog post will both prove you’re wrong and agree with you. Plus, we’ll teach you what every change Google made so far in 2018 is doing to your site and how you can improve your marketing and SEO moves.

After a year like 2017 with significant algorithm changes and updates, Google doesn’t seem to want to settle down. Danny Sullivan, the officially-appointed ombudsman from Google, made it clear that they do various minor updates daily plus some more serious ones during the year: We do some type of focused update nearly daily. A broad core algorithm update happens several times per year.
Guess this is how we could explain the hectic fluctuations in various Google algorithm monitoring tools. Webmaster and marketers alike often felt overwhelmed by the density and frequency of these ranking fluctuations and tried to interpret their activity, correlating their analysis and findings, and reaching a conclusion or providing an educated guess until Google would have officially confirmed them.
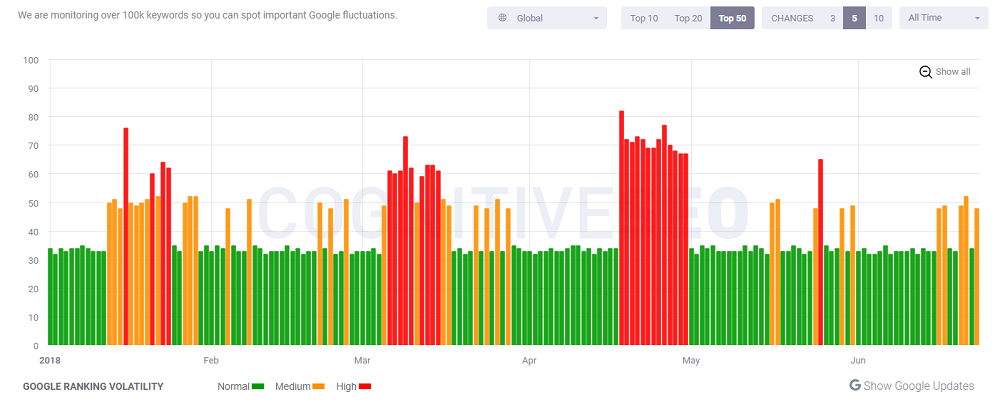
Screenshot taken from cognitiveseo.com/signals
Google likes messing around with people’s website traffic and site owners’ feelings – it sort of gives people mixed feelings regarding Google: both love and hate.
Many updates or changes in the way Google’s algorithm works is given by an interesting paradigm skillful webmasters know how to read. And that is the one provided by Barry Schwartz, the update guru of our digital marketing world:
| When you have both signals, SEO chatter, and tools start lighting up, it is a good sign something major changed in the core ranking algorithm with Google search. | |
 |
BARRY SCHWARTZ |
| Founder at Search Engine Roundtable @rustybrick / rustybrick.com | |
The 2018 updates pace is pretty aggressive, one might say, while March seems to have been the busiest month in terms of changes and ranking fluctuations. We’re not talking officially announced updates here, but only the SERPs activity as seen in forums and Google algorithm updates tracking tools.
Talking about Google-confirmed updates, it’s quite seldom for Google to officially confirm updates; it only happens several times a year. As a result, many updates that impacted websites across the world wide web might not be named and talked about as much as those regarded as significant by the Googlers. A fit example would be the March 7 one, widely known as a core algorithm update meant to reward “the under-rewarded sites”, as some webmasters would say. It has greatly impacted traffic and rankings while also needing a longer time span than usual.
| The specifics of Google’s algorithm will always remain under wraps. | |
 |
SAM GOWING |
| Writer at Fifty Five and Five @_SamGowing / fiftyfiveandfive.com | |
However, even when Google does give official statements about one update or another, they are quite evasive when it comes to confirming or guide users through. Maybe that’s why Barry Schwartz often says: “The answer, according to Google, is really nothing”.
Whenever site owners or fellow marketers want to dig more into what it looks like being an algorithm change, they turn to Barry Schwartz, as the go-to high-quality source regarding monitoring, researching, analyzing, and dissecting Google both confirmed and unconfirmed updates. Even though Barry’s posts often start as being speculative, they’re nonetheless worth checking them out and following him as they usually get confirmed later on either by fellow webmasters or by the Google team itself.
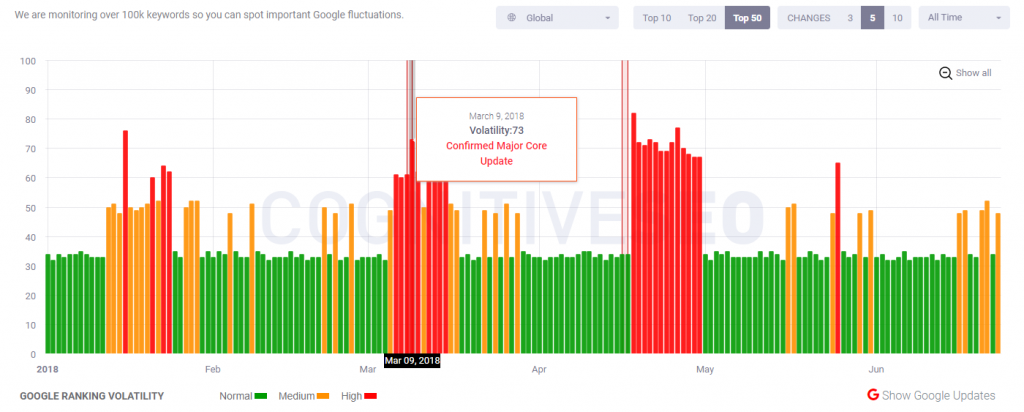
Either way, be the update Google-confirmed or unconfirmed, bearing a name or not, impacting websites over a shorter or longer period of time, it’s clear that there are fluctuations and while some sites might see drops in traffic, others might notice gains. As a consequence, both the lucky and the unfortunate sites should neither rub their gain in, nor lose confidence, but stick to building great content that makes searcher want to return to your page.
Without further ado, we shall talk about the 2018 Google updates that happened so far, focusing on those that were Google or webmasters-backed and already influenced the traffic and ranking flow of many websites.
This update happened in the first month of 2018. Usually, December comes with a good share of inactivity, but this last December 2017 proved to be quite busy, were we to look at all the updates that have rambled on the Google streets: the Google-confirmed Maccabees updates that made a target out of some celebrity sites as well, knowledge graph updates, SEO starter guide update, extended meta description space, rich results testing tool new release and many more.

Mobile Page Speed as a Ranking Factor
source: seroundtable,com
Getting back to our sheep, January 18 was marked by a Google-official announcement that regarded a page speed update scheduled to come into effect this July (we’d better hurry and make the right changes to our site, don’t we?). Google said this is a new ranking algorithm designed to lower the SERP position of some mobile pages that deliver a really slow experience to the end user.
Therefore, here we have it: a brand new, officially-announced Google ranking algorithm: page speed. Starting July 2018, page speed will be a ranking factor for all mobile searches.
Slow mobile pages that will get hit by this update will most likely not be notified in the Google Search Console given that this is an algorithmic thing, not a manual action. The good news, though, is that Google forecasted their actions to hit only a small percentage of pages presenting the slowest loading time and therefore a handful of queries. Schwartz, too, thinks this update is not very disruptive given that a page would have to be super slow to really get hit by this major update.
| To be clear, there is no ranking boost for being fast, just a downgrade for being really slow. | |
 |
BERRY SCHWARTZ |
| Founder at Search Engine Roundtable @rustybrick / rustybrick.com | |
Apart from what we’ve previously said above – that it won’t impact the traffic and rankings lest you provide (at least) a reasonably satisfactory and fast experience to your users (which comes pretty obvious),- some webmasters raised a question: what comes first – canonical URL or AMP URL? This comes after many started worrying on how big of an impact will this update cause on their sites.
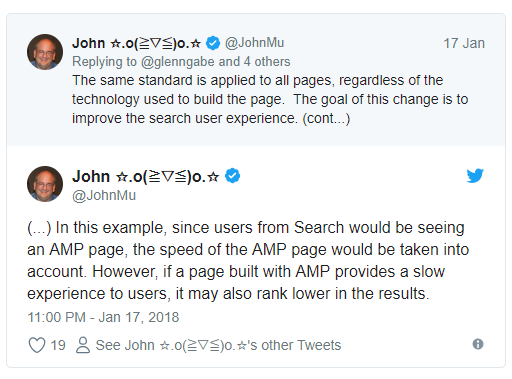
If a page’s canonical page is very slow but the AMP URL is very fast, will Google use the AMP or the mobile URL for measuring speed and ranking the page? Although, in theory, Google uses the canonical URL regardless whether there’s a desktop or mobile page involved and they have an AMP URL, Google confirmed that since the AMP URL is provided and is mega-fast, then no downgrade in rankings will take place. Berry’s answer is this:
| The answer is AMP for speed will be what Google uses for this algorithm, not your canonical URL because that is what is being served. But for other signals, like content, links, etc, Google will use the canonical mobile URL. Confused? Yeah, thought so.” | |
 |
BERRY SCHWARTZ |
| Founder at Search Engine Roundtable @rustybrick / rustybrick.com | |
What’s more, many Google users confuse this new speed ranking update with the Mobile-First Indexing update – they’re independent from one another, so don’t mingle them.
Last but not least, this January/July major ranking update will not boost the rankings of those pages that are fast, but only downgrade those that are extremely slow.
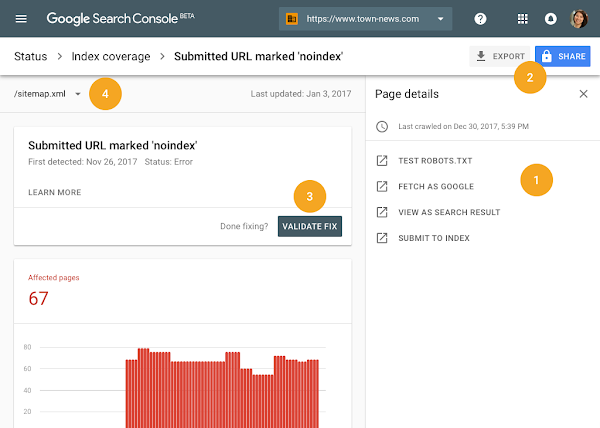
This update seemed to drive people crazy after Google: digital marketers and webmasters alike were very happy to learn that starting on January 8, the search giant released a new version of their Search Console with 16 months of stored data.
Besides Google Search Console Beta getting live for everyone with 16 months of stored data in the Search Performance report, Google also added various enticing new features to this version, such as an updated Index Coverage report (alerting you when bumping into new issues and helping you monitor their behavior), and a changed AMP status and Job Posting report.
Everybody can now understand how to optimize their site for Google, given how simple everything is (or at least it seems). In addition, having an extended period of data storage, you can now deploy more in-depth analysis of long-term trends that might impact more than one year. You will be able to work with really actionable data and make a wiser decision regarding your website and the overall user experience.
source: webmasters.googleblog.com
Also very important is the fact that the Google team intends to make this Google Search Console updating process a long-term one, hence they will continue adding new features and changes to their version. As a consequence, the Google team is asking for continued feedback – after all, how do you think the new GSC version got launched?
Danny Sullivan, Google’s public search liaison, decided to create a brand new Twitter profile meant to inform, guide, explain, and be in contact with all Googlers and users and announced it on January 26. Most of us already got those from following Danny’s profile but he found it more suitable to deliver messages regarding Google search on an entirely new profile and spare his following of Star Wars and Star Trek tweets, should they be interested mostly in the search side.
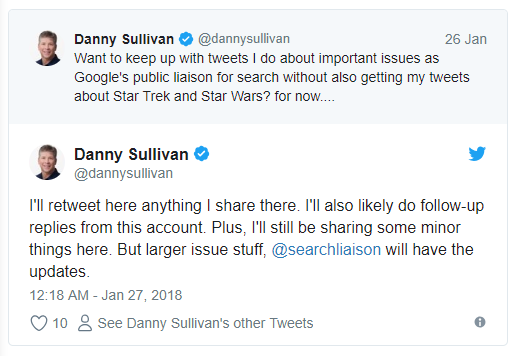
While this isn’t really a Google algorithm or ranking update, it still counts as a smart move meant to benefit all of the Google fans out there. I myself am quite thankful for this twist of events and seek to follow the Google SearchLiaison profile as closely as possible.
Why, you might wonder. Well, simply put, as Berry Schwartz is the primary source to check when it comes to Google updates in general, such is the new Google SearchLiaison profile the go-to source of information when it comes to every search-related thing, explanation, debate, or piece of news.
This security-centric turn comes to prove once again the Google really cares about the user experience and trust websites provide to their visitors. Similar to the page speed update mentioned earlier, Google announced on February 9 that starting July 2018, websites should have an SSL addition to their site and provide an HTTPS-backed experience to their users, or else they’ll be punished.

source: searchenginejournal.com
This HTTP-to-HTTPS issue is twofold: first, it’s for your own good and safety to use HTTPS instead of HTTP (“S” actually comes from “security”), two, Google will straightforwardly warn your visitors that your website is not safe browsing, leading to a pretty high bounce rate.
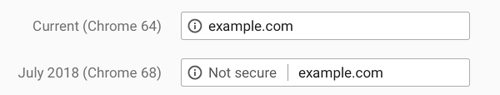
source: searchenginejournal.com
Given that Chrome holds a good browser version market share of 50% worldwide, we can say this update will impact many web owners. Therefore having a protruding notice in the Omnibox warning users that your website is “Not secure”, might increase bounce rate and take a toll on advertising impressions, affiliate links, and e-commerce overall sales. Here’s a list pointing out how many Chrome users there are and the impact level this update might have on various regions and countries, should website not switch to HTPPS.

source: searchenginejournal.com
Switching to HTTPS might be a bit difficult but it pays off. Most web hosting providers already provide this service for free or manage to give you HTTPS certificates at a rather low cost. So you have no excuse postponing this as money shouldn’t really be a problem.
This Google change got live on February 13 and got fully implemented on desktop search already. Somehow, it’s similar to “people also ask” section except that this one directs people to other SERPs.
The new look is one search refinement meant to benefit organic results. Should you not qualify for a keyword entered in a search query, Google could lead visitors to your site when offering them variations of the first query. Or the other way around: if you focused on optimizing your page content and used both short and long keywords that might answer to a vast array of queries, you might appear twice in SERPs.
Starting February 19 this year, Chrome v64 cuts off unnecessary tails and the end of an URL when sharing it using the URL streaming “Share” in Chrome.
Berry Schwartz had a feeling that this new feature is tied to the canonical page URL. AMP has similar sharing features in order to deliver an easy-to-use and relevant URL.
Besides the impact we’ve mentioned above, the one with using and delivering a usable URL, there are two more consequences to this update.
On one hand, having the original URL trimmed when shared could be a little annoying, given that when it opens the page, it would load only the top of the page and lose the specific location it had when attached to, say, the anchor text.
On the other hand, who knows, maybe this feature will become really useful at some point in the future.
One major update from Google happened on February 19 when the giant search engine radically changed the Search Console crawl limits due to spam and abuse.
Although there’s only a small percent who could abuse the system, it happened nonetheless and the team had to take action.
The Search Console limits per option changed:
Google Search Console also changed numbers here:
Barry Schwartz thinks this update might not be such a big deal to white-hat SEOs who don’t use this tool so often, given that a submission for indexation normally happens on a limited basis. But it might block some spam and unnatural activity from black-hat users.
This Google update birth story is quite a soap opera. Once upon a February 22 day, webmasters and digital marketers alike gave a shoutout to a big announcement Google made at PubCon regarding a new ranking algorithm. Gary Illyes from Google announced onstage that the search engine webmaster team intends to roll the mobile-first index for more sites in the following weeks.
The mobile-first indexing update didn’t come into effect until around March 26, as John Mueller didn’t give an exact date regarding the full start. Those monitoring fluctuations in Google rankings and traffic couldn’t tell either when exactly this updated started given the quite lengthy period of activity. What’s more, it almost gone completely unnoticed as there were few to no sites to signal their new ranking position from which to determine whether they were hit by this update or not.
To best explain this update and what it does to your site, we could say that mobile-first indexing points out to Google’s attempt at indexing and ranking your website from a mobile point-of-view, when applicable. That is, should you have a mobile-friendly website, Google would index and rank your mobile version first. When I said “when applicable” it meant that Google will treat the world wide web this way only when bumping into sites that follow the best practices required by mobile-first indexing, therefore wouldn’t impact the other websites that didn’t check this aspect on their list. At least for now.
| We evaluate each site individually on its readiness for mobile-first indexing based on the best practices and transition the site when the site is ready. | |
 |
GOOGLE SEARCH |
| developers.google.com | |
This update is a global and multilingual rollout, thus it’s meeant for everyone and will impact everyone.
Regardless if your website is ready from a mobile-friendliness standpoint or not, optimizing and having mobile-friendly content is still relevant in marketing strategies that seek to make the website perform better in SERPs. Given there is a vast array of ranking signals that may influence your position in search, you might deliver content that is not necessarily mobile-friendly or is slow-loading. Having said this, optimizing your website for mobile would set your marketing strategy on fire, so you should definitely not postpone it.
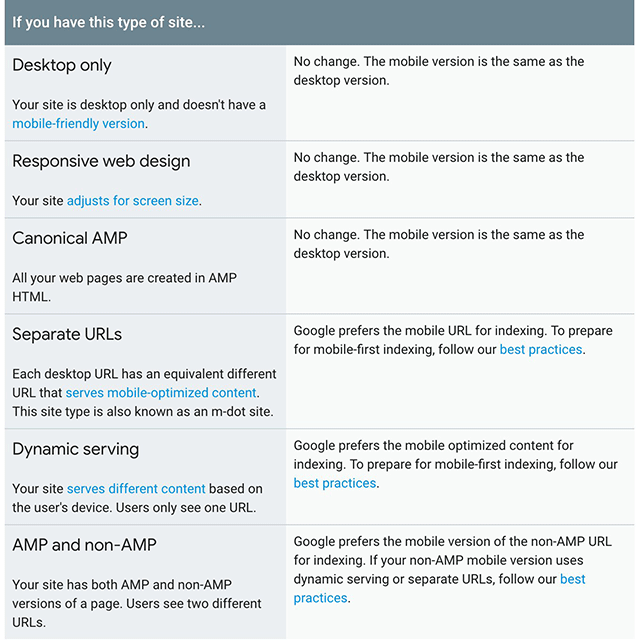
N.B.: This update is mobile-first indexing, not mobile first index, where the primary index is still the desktop one, this one only being added to the core one.
A new form of featured snippets was released on March 1 and it’s meant to answer queries that might be driven by more than one need and search intent.
Google said they intend to provide more than one featured snippet for queries that might serve or have several potential intentions or purposes associated. This is one more step forward in what Google is trying to better understand the users and update it’s AI algorithm to deliver the best and the most satisfactory result possible.
Having a Google update such as multifaceted featured snippets is great news for both site owners and content marketers. This means that more sites will get the chance to be featured on position 0 in SERPs.
Site owners will have a double shot at ranking high in search while content marketers’ efforts of optimizing their content in order to be featured up there, will finally be rewarded.
On the other hand though, I sense this update might be a bit nagging to the user, given that this will only get the page more crowded than it already is.
On March 9, there were some unnamed updates, yet online marketers knew how to interpret them and realize how big it was. while inquiring Google webmasters. John Mueller from Google confirmed in a Webmasters Hangout that these updates had to relevancy:
| The updates that we made are more about relevance where we’re trying to figure out which sites relevant for certain queries and and not so much quality overall. It doesn’t means its a bad sign, we may just be finding that your site isn’t relevant for these particular queries. | |
 |
JOHN MUELLER |
| Webmaster Trends Analyst at Google @JohnMu | |
Marie Haynes and her team investigates several site that got hit on March 9 and noticed similarities among most of them. Many of the victims were relatively big brand who lost rankings on their articles, which , on a closer look, showed signs of duplicate content in regard to other sites’ content. This clearly pointed out the fact that Google intends to sift sites that don’t raise up to the standard of providing helpful, useful, and unique content on their pages.
| This is not an update pointing to who is bad and who is good – but they rather seek to refine their answers to people’s queries – hence, they want to give the good answer not just the one that ranks for it. | |
| MARIE HAYNES | |
| Blogger @Marie_Haynes / hiswebmarketing.com | |
Seeing a drop around March 9 might show you were hit by this relevancy update. Getting downgraded doesn’t necessarily mean that your content is awful, but because Google saw one or more of your competitors being more qualitative than you.
Should you start optimizing your content and trying to fix everything so to see results as soon as possible won’t help you on the spot. When refining your marketing strategy, start with a site audit, read the Quality Raters’ Guidelines very carefully, and ask someone who’s close to you but unfamilliar with your website to compare you with your competitors and tell you what they see, and last but not least, cut off from duplicate content.
If Google has a hard time reading JavaScript Sites, then this update comes as a great surprise and a piece of great newson March 10. Tom Greenaway from Google, at Google I/O 2018 said that Google approaches indexing and ranking of JavaScript pages very differently than non-JavaScript ones.
In more human words, the Googlebot might have issues indexing and rendering the contents of a JavaScript page and might need to do it in more than one wave. Hence, Javascript powered website in Google are deferred until the fit resources to process that content.
And yet, Google worked their mobile-friendly and rich results rendering tools to be able to work with sites built in JavaScript language. In more technical words:
| Those tools can now both show the screenshots for JS-based sites, rendered DOM, show JavaScript errors and stack traces as seen by the Googlebot’s web render service. The tools will show rendered HTML, the console log, exceptions, and stack traces. | |
 |
BERRY SCHWARTZ |
| Founder at Search Engine Roundtable @rustybrick / rustybrick.com | |
Well, from now on, websites built in JavaScript will be readable from a mobile-friendly standpoint, while also appearing in rich snippets when somebody would enter a query from the mobile phone. Websites will double, if not triple their visibility, rank higher, and get increased traffic to their sites. This update is pretty much self-explanatory.
Many website owners complained about Google not mentioning where the carousel info was taken from so the switch is quite significant. Google added on April 11 a new featured to their carousel and is visible to both mobile and desktop end users.
source: seroundtable.com
When clicking on the carousel, it leads you not to the brand site but to the actual Wikipedia page of that brand or product.
It’s still not clear to what kind of searcher this carousel appears or in what country, yet one thing is clear. Big brands or websites that got featured in Wikipedia doubled their chances of appearing in Google SERPs.
What’s more, some searches trigger a featured snippet instead of a carousel, hence this is quite an intricate update.
Starting early this year, Google added new AdWords features almost every month: January, March, April, and May. In January, Google started allowing advertisers to add, edit, or remove keywords while they’re busy doing something else. Also, users have now the chance to quickly identify and name Display ads issues from the Overview page and find out more about every impression shift in search results. March had its fair share of new features, while April and May showed low activity with only one update each, April promising the chance of getting an insider look into keywords that aren’t showing ads together with an explanation, plus “get more done in less time”.
source: support.google.com
All these AdWords updates are meant to positively impact your advertising efforts and help you learn more from an environment you’re so much expecting results. Google’s aim is to allow you get deeper insight from your data in order to make the right selling decisions.
The updates that got launched so far in 2018 had to do a lot with user experience:
Google wanted pages to load fast (page speed), not have intrusive ads, lacking mobile optimization, and be relevant.
Even though, as Schwartz names them, many ranking fluctuations didn’t point out to a heavy or core update and were more some sort of “hiccups”, one thing is sure: Google is set to make their search engine as human as possible and as smart and cunning as a human being.
Every month, there has been a lot of chatter, debate, educated guesses in forums such as WebmasterWorld, Black Hat Forums, Google forums, as proved by the tools that monitor Google’s changes that mainly affect traffic and rankings (cognitiveSEO, SERPmetrics, Mozcast, Advanced Web Ranking, Accuranker, Algaroo, RankRanger, SEMRush).
Overall, we can expect more from Google as the time passes. Should you want to be ready for the upcoming updates or just fix your websites as much as you can for the ones that come into effect this July – page speed update and switching from HTTP to HTPPS -, make sure you read this post.
Google has one love and one heart: their users, and that’s why they’ll continue focusing on mobile that’s on the rise lately, improved user experience (UX), and richer and more relevant content experiences.
Unbelievable! Its comfort actually!
read moreAs time went by, this blog was developed for many different purposes. Last time, I had a lot of pleasure in sharing some of my Lego-related hobbies. However, I will mostly upload a blog about bikes and their development in the next few months! Recently, I have so much into ebike cargo. They say this type of bike can replace the car! And I am very into it since my place is crowded with traffic jams! The video above showed a funny situation: I started the review from Brooks's handle! And after nine years! It's still an excellent bike handle and not even destroyed!
read moreKeep Watching
Hi, hi, hi. So, it's been a while for the last couple of weeks since I have considered buying a cargo bike. The reason is that I am often trapped in a traffic jam because I can't get faster in my car.
read moreIndonesia has launched Southeast Asia’s first-ever bullet train, a high-speed rail line connecting two of its largest cities.Congrats! Indonesia launched Southeast Asia’s first bullet train.

Custom LEGO Transformers Devastator
My faith in humanity is restored! OK, that’s a bit overboard – but you couldn’t blame me if you see an incredibly, exquisitely and wonderfully executed custom LEGO Transformers Devastator such as this by Alex Jones. I feel transported to the 80’s once again, with the same intense childhood wonder when I first saw the Constructicons combine and become the formidable Devastator.

Collaboratively administrate empowered markets via plug-and-play networks. Dynamically procrastinate B2C users after installed base benefits. Dramatically visualize customer directed convergence without
Comments